This article focuses on the commonly used eight major temperature instruments to explain, from the working principle, to the installation requirements, as well as product selection and use of the process should pay attention to the problems, and the composition of the instrument, a detailed description of the common eight major temperature instrument, for Meter people provide theoretical and empirical help in later work!
Bimetallic thermometer
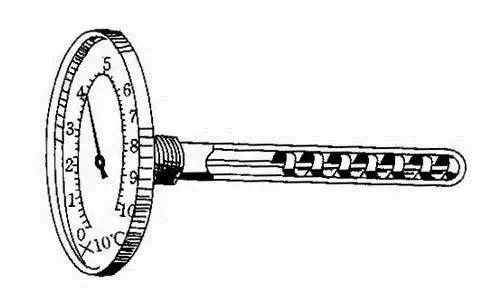
working principle:
The working principle of the bimetal thermometer is to use two kinds of metals with different temperature expansion coefficients. In order to improve the sensitivity of temperature measurement, the metal sheet is usually made into a spiral coil shape. When the temperature of the multi-layer metal sheet changes, the metal expands or shrinks in each layer. Unequal, so that the spiral roll up or loosen.
Since one end of the spiral coil is fixed and the other end is connected to a pointer that can rotate freely, when the bimetal feels a temperature change, the pointer can indicate the temperature on a circular graduated scale.
The temperature range of this instrument is generally between -80°C and +500°C, and the allowable error is about 1.5% of the scale range.
classification:
Ordinary bimetal thermometer, shock-proof bimetal thermometer, electric node bimetal thermometer.
According to the connection direction of the bimetal thermometer pointer disk and the protection tube, the bimetal thermometer can be divided into four types: axial type, radial type, 135° type, and universal type.
1 Axial type bimetal thermometer: The pointer plate is vertically connected to the protective tube.
2 Radial type bimetal thermometer: The pointer plate is connected in parallel with the protective tube.
3135° bimetal thermometer: The pointer plate is connected to the protective tube at 135°.
4 universal type bimetal thermometer: The connection angle between the pointer plate and the protection tube can be adjusted arbitrarily.
Selection and use:
In the selection of bimetal thermometers, full consideration should be given to the practical application environment and requirements, such as the diameter of the dial, the accuracy level, the mounting and fixing method, the type of the measured medium, and the environmental risk. In addition, factors such as cost-effectiveness and maintenance workload should also be considered.
In addition, the bimetal thermometer should pay attention to the following points during use:
A, bimetal thermometer protection tube immersed in the measured medium length must be greater than the length of the temperature sensing element, generally immersed in length greater than 100mm, 0-50 °C range immersion length greater than 150mm, in order to ensure the accuracy of the measurement.
B, all kinds of bimetal thermometers should not be used to measure the temperature of the medium in open containers, live contact thermometers should not be used in the control loop of the occasion where the work vibration.
C. When the bimetal thermometer is stored, used, installed and transported, collision protection tubes should be avoided. Do not bend the protection tube and use it as a wrench.
D. The thermometer should be tested regularly under normal use. It is generally appropriate every six months. Electrical contact thermometers are not allowed to work under strong vibrations so as not to affect the reliability of the contacts.
E. The temperature at which the instrument often works can best be within 1/3 to 2/3 of the scale range.
Pressure thermometer
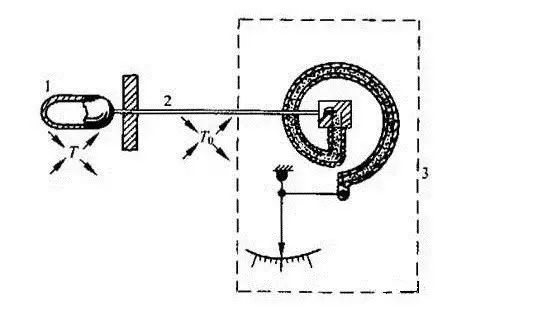
working principle:
The principle of the pressure type thermometer is based on the relationship between the saturated vapor pressure and the temperature of the evaporating liquid in the closed temperature measurement system, and the temperature measurement is performed. When the warm package feels a temperature change, the saturated vapor in the closed system generates a corresponding pressure, causing the elastic component to change its curvature, causing its free end to undergo displacement, and then the gear amplifying mechanism changes the displacement to an indicated value.
Composition and classification:
The pressure type thermometer is composed of a temperature sensing element, a pressure transmitting capillary and a spring tube pressure gauge.
If the system is filled with gas, such as nitrogen, called inflatable pressure type thermometer, the upper limit of temperature measurement can reach 500°C. The relationship between pressure and temperature is close to linear, but the temperature of the package is large and the thermal inertia is large.
If it is filled with liquids, such as xylene, methanol, etc., the temperature will be smaller and the temperature range will be -40°C~200°C and -40°C~170°C, respectively.
If filled with low-boiling liquids, the saturated vapor pressure should be changed with the measured temperature, such as acetone, for 50 °C ~ 200 °C. However, since the saturated vapor pressure and the saturated vapor temperature are nonlinear, the thermometer scale is not uniform.
Features:
All temperature packages must be immersed in the measured medium; the longest capillary does not exceed 60m; the instrument accuracy is low, but it is easy to use and resistant to vibration.
Resistance thermometer

working principle:
The principle of temperature measurement of the thermal resistance is to measure the temperature or temperature-related parameters based on the characteristics that the resistance value of the conductor or the semiconductor changes with the temperature change.
The resistance of most metals varies with temperature. The higher the temperature, the greater the resistance, ie, the positive temperature coefficient of resistance. While most semiconductor materials have a negative temperature coefficient of resistance, the higher the temperature, the smaller the resistance.
Composition material requirements
1. The chemical and physical properties are stable within the range of temperature measurement;
2, good reproducibility;
3, resistance temperature coefficient, in order to obtain high sensitivity;
4, high resistivity, can get small-sized components;
5, resistance temperature characteristics as close as possible to linear;
6, low prices.
Commonly used thermal resistance elements:
Commonly used thermal resistance elements are: platinum thermal resistance, copper thermal resistance, semiconductor thermistor.
Platinum thermal resistance is made of high-purity platinum wire. It has the advantages of high accuracy in temperature measurement, stable performance, good reproducibility, and resistance to oxidation. Therefore, it is widely used in reference, laboratory and industry. However, it is easily contaminated by a reducing atmosphere at a high temperature, making the platinum wire brittle and changing its resistance temperature characteristics, so it needs to be protected by a bushing before use. Platinum wire purity is the key to the accuracy of the thermometer. The higher the purity of the platinum wire, the higher its stability, the better the reproducibility, and the higher the accuracy of temperature measurement.
The resistance value of the copper thermal resistance is close to the temperature, and the temperature coefficient of the resistance is also relatively large, and the price is low. Therefore, in the case where the measurement accuracy is not very high, the copper thermal resistor is often used. However, it is easily oxidized in an atmosphere higher than 100°C, so it is mostly used for measuring a temperature range of -50 to 150°C.
Semiconductor Thermistor Advantages: Negative temperature coefficient of resistance, so high sensitivity. Resistivity is high, can make the resistance element that the volume is small and the resistance value is large, this makes it have thermal inertia small and measurable point temperature or dynamic temperature. Disadvantages: The same type of semiconductor thermistor's resistance temperature characteristics of dispersion, non-linear serious, component performance is not stable, so poor interchangeability, low precision.
Thermal resistance connection:
Two-wire system: The method of connecting a wire to the two ends of the RTD to induce the resistance signal is called two-wire system. This wire method is very simple, but because the connection wire must have the wire resistance R, R size and the material and length of the wire. Depends on the factors, so this lead wire method is only suitable for occasions with low measurement accuracy
Three-wire system: The method of connecting a lead wire at one end of the root of a thermistor and connecting the two leads at the other end is called a three-wire system. This method is usually used in conjunction with a bridge to eliminate the influence of the lead wire resistance. The most commonly used in process control.
Four-wire system: The method of connecting two wires at both ends of the thermal resistor is called four-wire system, in which two wires provide a constant current I for the thermal resistance, converts R into a voltage signal U, and then passes the other two wires. Lead U to the secondary instrument. It can be seen that this lead wire method can completely eliminate the influence of the resistance of the wire, and is mainly used for high-precision temperature detection.
Installation requirements:
For the installation of thermal resistance, it should be noted that it is conducive to accurate temperature measurement, safety and reliability, and easy maintenance. It does not affect equipment operation and production operations. Please pay attention to the following points when selecting the installation location and insertion depth of the thermal resistance:
1. In order to make sufficient heat exchange between the measuring end of the thermal resistance and the measured medium, the location of the measuring point should be reasonably selected to avoid installing the thermal resistance near the dead ends of the valves, elbows, pipes and equipment.
2. The thermal resistance with protection sleeve has heat transfer and heat loss. In order to reduce the measurement error, the thermocouple and thermal resistance should have enough insertion depth:
1) For measuring the thermal resistance of the fluid temperature in the center of the pipeline, the measuring end should generally be inserted into the center of the pipeline (vertical or inclined installation). If the pipe diameter of the fluid to be measured is 200 mm, the insertion depth of the thermal resistance should be 100 mm;
2) For the temperature measurement of high temperature, high pressure and high speed fluids (such as main steam temperature), in order to reduce the resistance of the protective sleeve to the fluid and prevent the protective sleeve from breaking under the action of the fluid, the protection tube can be inserted in a shallow insertion manner or a hot sleeve type can be adopted. Thermal resistance. Shallow plug-in thermal resistance protection sleeve, the depth of its insertion into the main steam pipe should not be less than 75mm; standard insertion depth of hot-set thermal resistance is 100mm.
3) If it is necessary to measure the temperature of the flue gas in the flue, although the diameter of the flue is 4m, the insertion depth of the thermal resistance can be 1m.
4) When measuring the depth of the original inserted more than 1m, it should be installed as far as possible vertical, or install support frame and protection sleeve.
Thermocouple thermometer

working principle:
Two different components of the conductor (called a thermocouple wire or a hot electrode) are joined together at both ends. When the junction temperature is different, an electromotive force is generated in the circuit. This phenomenon is called the thermoelectric effect. The electromotive force is called thermoelectric power. Thermocouples use this principle for temperature measurement, in which the end that is used directly to measure the temperature of a medium is called the working end (also called the measuring end), and the other end is called the cold end (also called the compensation end); the cold end and the display The meter or associated meter is connected and the meter indicates the thermoelectric potential generated by the thermocouple.
Installation requirements:
First, the installation of thermocouples and thermal resistors should be kept as vertical as possible to prevent deformation of the protective sleeve at high temperatures. However, in the case of flow velocity, it must be inserted in the direction of the measured medium to ensure that the temperature measuring element is The full contact of the fluid ensures its measurement accuracy.
In addition, thermocouples and thermal resistors should be installed in the protected pipeline to prevent heat loss. Secondly, when the thermocouple and the RTD sensor are installed in the negative pressure pipeline, it must be ensured that the measurement area has a good seal to prevent the external cold air from entering and make the reading low.
When the thermocouple and RTD sensors are installed outdoors, the junction box cover of the thermocouple and RTD sensor should be upward, and the inlet should be downward to prevent rain or dust from entering the junction box, and damage the thermocouple and the RTD wiring. The wiring inside the box affects its measurement accuracy.
Should always check the thermocouple and the resistance thermometer around the wiring situation, especially the thermocouple thermometer due to the high hardness of the compensation wire material, it is very easy to break off from the terminal to cause circuit failure, so to be well connected not to touch the thermometer too much The wiring and always check to get the correct measurement temperature.
The thermocouple should be placed as close as possible to the temperature control point to be measured. To prevent heat transfer along the thermocouple or prevent the protection tube from affecting the measured temperature, the thermocouple should be immersed in the fluid under test, at a depth of at least 10 times the diameter. When measuring the solid temperature, the thermocouple should be against or in intimate contact with the material. In order to minimize the thermal conduction error, the temperature gradient near the contact should be reduced.
When thermocouples are used to measure the gas temperature in a pipe, if the wall temperature is significantly higher or lower, the thermocouple will radiate or absorb heat, significantly changing the measured temperature. At this time, a radiation shield can be used to bring its temperature close to the gas temperature, using a so-called shield thermocouple.
The temperature measurement point should be representative. For example, when measuring the fluid temperature in the pipeline, the measuring end of the thermocouple should be at the maximum flow rate in the pipeline. In general, the end of the thermowell's protective sleeve should cross the flow centerline.
Glass tube liquid thermometer

working principle:
Glass liquid thermometers use the thermal expansion and contraction effect of the temperature measurement principle: When the temperature changes, the liquid volume in the glass ball will expand or shrink, so that the height of the liquid column into the capillary changes, from the scale can indicate the temperature Variety.
The scale resolution of the thermometer is related to the sensitivity of the thermometer. With high sensitivity, the scale of the thermometer is high in resolution. To increase the sensitivity of the thermometer, increase the volume of the thermometric fluid or reduce the diameter of the capillary. However, increasing the volume of the temperature measuring fluid does not easily achieve thermal equilibrium with the measured substance, resulting in a large lag error and easily deforming the ball; decreasing the diameter of the capillary tube makes the capillary not easily processed evenly, resulting in the rise of the liquid column. Uneven, affect the accuracy of the measurement. Therefore, appropriate sensitivity should be taken.
In addition, the sensitivity of the thermometer is also related to the difference between the thermal expansion coefficient of the temperature measuring fluid and the glass and is proportional to the difference. Generally, a liquid having a large thermal expansion coefficient is selected as a temperature measuring liquid, and the thermal expansion coefficient of the glass should be as small as possible. Commonly used temperature measurement fluids are mercury and alcohol.
The main cause of error:
(1) Zero displacement forever
(2) Temporary deformation of the ball
(3) Pressure changes
(4) Inaccurate scale
(5) The reading method is incorrect
(6) Thermal hysteresis effect
(7) Special causes of errors in alcohol thermometers
(8) Special causes of errors in the highest thermometer
Temperature Transmitter

working principle:
The temperature current transmitter converts the temperature sensor signal into a current signal and is connected to a secondary meter to show the corresponding temperature. The temperature transmitter adopts thermocouple and thermal resistance as the temperature measuring element, and the output signal from the temperature measuring element is sent to the transmitter module, after filtering, arithmetic amplification, nonlinear correction, V/I conversion, constant current and reverse After the protection circuit is processed, it is converted into a 4-20mA current signal output that is linear with the temperature.
Installation requirements:
1, before installation, check whether the accessories are complete, whether there is loose fasteners, tighten the antenna.
2, when installing, pay attention to gently, do not knock, fall. Tighten the antenna to work properly
3. After installation, after the power is turned on, non-operators are prohibited from opening the front cover. If the operator erroneously operates the front cover, it is forbidden to save it. After the power is turned off, it can be turned on again.
The main cause of error:
Transmitter output does not change when the temperature of the measured medium increases or decreases. This situation is mostly a problem with the temperature transmitter sealing, which may be due to the temperature transmitter not sealing or accidentally welding the sensor during welding. A small hole, this situation generally need to replace the transmitter shell to solve.
The output signal is not stable. This is the reason for the temperature source. The temperature source is an unstable temperature. If the meter display is unstable, it is the reason that the instrument's anti-interference ability is not strong.
Transmitter output error is large. The reason for this is more. It may be that the resistance wire of the selected temperature transmitter does not cause range error, and there may be no calibration when the transmitter is shipped.
Temperature Switches

working principle:
The temperature switch is a temperature switch using a bimetal as a temperature sensing element. When the electrical appliance works normally, the bimetal is in a free state, the contacts are in a closed/open state, and when the temperature is increased to an operating temperature value, the bimetal is The element generates heat due to internal stress and acts quickly, opens/closes the contact, cuts/makes the circuit, and thus acts as a thermal protection. The contact automatically closes/opens when the temperature is gradually reduced to the re-determined temperature, returning to normal operation.
Installation requirements:
1. When using contact-temperature-type installation, the metal cover should be tightly attached to the mounting surface of the controlled device. To ensure the temperature-sensing effect, thermal grease or other similar heat-conducting medium should be coated on the temperature-sensitive surface.
2. Do not collapse, loosen or deform the top of the cover during installation to avoid affecting performance.
3, can not let the liquid infiltrate the temperature controller inside, not to crack the shell, can not freely change the shape of the external terminal.
4, the product is used in the circuit of not more than 5A current, should choose the copper core section is 0. 5-1mm2 wire connection; not more than 10A electric current circuit, should choose the copper core section to be 0.75-1.5mm2 wire connection.
5. The product should be stored in a warehouse where the relative humidity is less than 90 [[%]] and the ambient temperature is below 40°C in a ventilated, clean, dry, non-corrosive atmosphere.
Optical, radiation pyrometer

working principle:
The radiation pyrometer is designed and manufactured according to the function relationship between the radiant energy and the temperature of the object in the whole wavelength range. The radiation temperature sensor is used as a meter, and the electronic potentiometer is used as a secondary instrument. It belongs to the lens focusing temperature sensor. The device has an aluminum alloy shell, the front part is an objective lens, the thermopile compensation light beam is installed in the shell, and a shifting plate is arranged on the field diaphragm of the thermopile. The role of the baffle is to regulate the irradiation on the thermopile. The radiant energy enables the product to have a uniform index value. An eyepiece is mounted on the removable rear cover to observe the image of the measured object.
The radiant thermal sensor focuses the radiant energy of the measured object on the thermal element through the lens. The thermal element converts the radiant energy into electrical parameters. The relationship between the known thermal potential and the temperature of the object is measured by the secondary instrument. The output of the thermal potential shows the temperature value. This temperature value must be corrected by the total radiation black system number of the object or directly inserted into the high-temperature salt bath furnace with a platinum rhodium 10-platinum thermocouple to measure the temperature with a dc potentiometer. Displays the temperature contrast to calibrate the accuracy of the pyrometer to measure the temperature.
Optical fiber thermometer, fiber optic fiber for short: It transmits a large amount of information at high speed and high reliability. It is immune to electromagnetic interference, good insulation, safe explosion-proof, low loss, transmission frequency bandwidth, large capacity, fine diameter, light weight, and flexibility. The advantages of curvature and corrosion resistance are applied to the field of signal detection. At present, the most used optical fiber is glass fiber, which is made of quartz glass filament that is thinner than hair.
It consists of a light-guiding core and its surrounding cladding. Outside the cladding, there are often protective covers such as plastic or rubber.
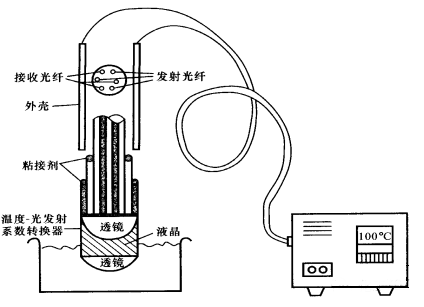
Installation requirements:
The instrument is a fixed installation type, and the temperature sensor can be used in an environment of 10 to 80°C. When the ambient temperature exceeds 80°C or the air medium contains water vapor and smoke, auxiliary equipment such as water cooling and ventilation can be used to reduce the ambient temperature. Purge the flue gas in the measurement channel to reduce measurement errors.
The temperature sensor auxiliary device is divided into light and heavy type. Heavy-duty is used in the harsh environment, in order to prevent the flame or high-temperature furnace gas in the furnace to be tested from burning out of the measurement channel and burn the instrument. The flame-proof device is installed to automatically operate in the event of danger to protect the instrument. And send an alarm signal.
Non-contact infrared thermometer

working principle:
Non-contact infrared thermometers (hereinafter referred to as “thermometersâ€) can determine the surface temperature by measuring the infrared energy radiated from the target surface.
Non-contact infrared thermometer uses ultra-low power smart design. The ultra-low power design ensures that the product can work for a longer period of time, reducing the user's trouble of frequent battery replacement and lack of power during work. The intelligent design helps the user to more easily test and capture the true value of the measured object more quickly. At the same time, the instrument can intelligently select the battery or USB connection for power supply.
Blade Fuse is a kind of current fuse, when the circuit current exceeds the fuse rated current of 2 times in a few seconds when the fuse will play the role of circuit protection. Widely used in equipment circuit protection standard for foreign and domestic automobiles and trucks. Readily identifiable and easily replaced, this fuse can be specified for a variety of low voltage electronic Applications.
Harness Component
Dongguan YAC Electric Co,. LTD. , https://www.yacentercn.com