With the development of the Internet of Things, edge computing has become one of the hottest technologies nowadays, attracting industry giants such as Huawei, Ali, ARM, and Intel. So where is marginal computing in the end and what is the relationship with the Internet of Things? And see below.
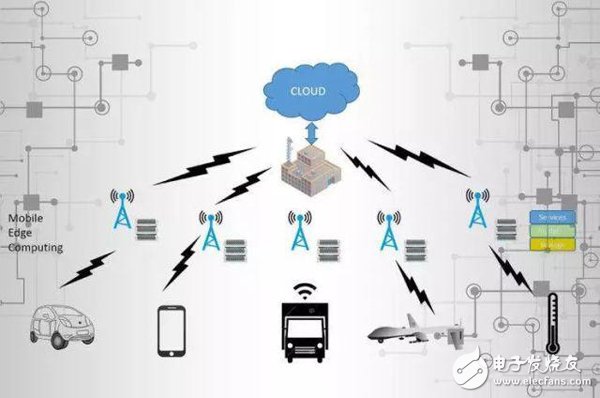 I. Cloud Computing IoT Challenge
I. Cloud Computing IoT Challenge As the most important platform technology of the Internet, cloud computing can build large-scale data centers, store and process large amounts of data in a centralized manner, and use the power of massive data center machines to calculate and solve problems.
Since the emergence and widespread use of cloud computing models at the beginning of this century, cloud computing has changed our lives, learning and work. From Guizhou to Iceland, the data centers of large companies can be seen all over the world. For Amazon, Microsoft, Ali and Tencent, the cloud computing platform has also become a very important source of business and revenue.
However, with the advent of the Internet of Things, cloud computing platforms will face challenges such as massive device access, massive data, insufficient bandwidth, and high power consumption. As far as the current bandwidth level is concerned, data transmission from the device to the cloud cannot be supported. This makes the decision of the cloud computing center to return data in real time becomes an impossible task.
As a result, edge computing began to enter the public's line of sight.
Second, the application of edge computing and its advantagesEdge computing is an open platform that integrates networks, computing, storage, and application core capabilities at the edge of the network near the source or data source. The core of edge computing is to migrate computing tasks from cloud computing centers to edge devices that generate source data.
The edge computing IoT solution is divided into: sensor control layer, network layer, agile controller and application layer.
Sensing control layer: This layer contains a large number of sensors, control components (such as switches, etc.) and measurement components (such as electricity meters, etc.), as well as communication components. These communication components may be independent or may be combined with other components.
Network layer: This layer mainly achieves convergence and interconnection. In addition to network connectivity and management, it also includes edge computing, on-site processing, and at the same time ensuring the survival of the business in the local area. Local survival and on-site processing are very important for IoT, especially industrial and civil large-scale facilities. In addition, protocol conversion is also an important feature of this layer. There are a lot of agreements in the IoT domain. These agreements come from the historical accumulation of various industries. Therefore, they need to make protocol conversions at the gateway and carry the data on the IP network and transmit them to the outside.
Agile Controller: This layer processes the data sent from the gateway and sends it to the application layer. It also manages the underlying network, sensors, control components, measurement components, and computing resources, and provides automated tools for network deployment and configuration.
Business application layer: This layer is a variety of industry applications.
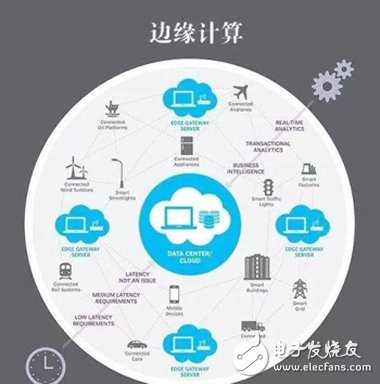
Since data is only exchanged between the source data device and the edge device and is no longer fully uploaded to the cloud computing platform, edge computing has absolute advantages in the following 5 aspects compared to traditional cloud computing in the application of the Internet of Things. :
Safety requirements
In the cloud computing model, all user data needs to be uploaded to the data center. In this process, data security becomes an important issue. From the electronic financial account passwords, to search engine history to smart camera monitoring, the privacy of these individuals' data is uploaded to the data center, all of which contain the risk of data leakage.
This is one of the reasons why edge computing has won the favor of large industrial companies. At Honeywell's User Group conference last year, most customers of its industrial automation products were reluctant to place wireless infrastructure in Honeywell's factory to avoid security breaches.
Various hacking behaviors due to Target's irregularities (starting from the HVAC system and eventually causing damage to the customer's credit card) triggered concerns about the infrastructure hackers, but for certain specific industrial processes, this Concerns are absolutely necessary.
2. Intellectual property issues
What's more, security issues are related to proprietary data and intellectual property concerns.
In cloud computing, all data of users needs to be uploaded to data centers, such as the refinery's oil refining process, production formulas of cola manufacturers, and other important information deemed as trade secrets, and industries that may be acquired through high-quality sensors. Data to get. According to Jaganath Rao, senior vice president of Siemens’ Internet of Things strategy, some food companies are particularly sensitive to this issue.
3. Interaction delay and flexibility
The amount of data faced in the Internet of Things application is huge, and it is no longer suitable for uploading directly to the cloud computing center for processing. Not only is the network bandwidth pressure high, but also the time-consuming search for massive data is unacceptable.
Self-driving cars have very high requirements for data transmission and interactive delays. Edge calculations are closer to the data sources. They can quickly process data and make decisions in real time, fully guaranteeing passenger safety.
In self-driving cars, each autonomous vehicle is equipped with multiple cameras and lidars. These sensors create large amounts of data every second. Auto-driving cars obviously can't wait for these data to be transmitted to the cloud computing center before making decisions. At this time, edge computing has become a weapon for unmanned real-time data processing. When the car is in danger of failure, the sensor can quickly send out faulty vibration information and send it to the local gateway for processing. The gateway issues an alarm or command within a few milliseconds or seconds after the fault is identified to shut down the machine.
In addition, this is also related to flexibility. In the case of vehicles, heavy industrial machinery, and manufacturing operations, the marginal computing can still ensure the survival of local networks, maintain continuous work, and avoid accidents when network coverage drops.
4. Reduce bandwidth costs
Some connected sensors (such as cameras or aggregate sensors working in the engine) can generate large amounts of data. In these cases, sending all of this information to the cloud can take a long time and cost too much.
With the need for smart cities and public safety, the importance of video analytics for cameras has emerged. However, due to the large number of cameras and the large amount of data generated, it is no longer suitable for direct upload to the cloud computing center for processing. Not only is the network bandwidth pressure, but also the time-consuming search for massive data is unacceptable. Come in handy.
5. Autonomy
It is due to the delay and elasticity problems that the autonomous decision-making of edge computing does not depend on the characteristics of the cloud, and it becomes the decisive advantage in the application of Internet of Things.
For many people, the purpose of the IoT connection factory or office is to be able to automate a large number of processes. In edge computing, the machine can not only monitor itself and the process it is performing, but it can also be programmed to take corrective actions when problems arise. Therefore, when the sensor detects pressure build-up, it can release further downward valves. Once the process relies on a specific level of automation, it must rely on this level to make timely decisions.
Third, the summaryEdge computing can provide intelligent interconnected services nearby to meet the industry's key requirements in the digital transformation process. In the 2.0 era of data processing in the IoT era, increasing data has created the need for edge computing. According to IDC, more than 50% of data in the future needs to be analyzed, processed, and stored at the edge of the network. Its huge market space is also seen by the giants. How will the future edge computing further promote the development of the Internet of Things? Let us wait and see!
Oil Filter For BUICK
Buick Oil Filter Replacement,Oil Filter For Buick,Buick Car Oil Filter,Buick Auto Oil Filter
Zhoushan Shenying Filter Manufacture Co., Ltd. , https://www.renkenfilter.com