The constant current source is a current source whose output current remains constant, and the ideal constant current source is:
a) Does not change due to load (output voltage) changes.
b) Does not change due to changes in ambient temperature.
c) The internal resistance is infinite.
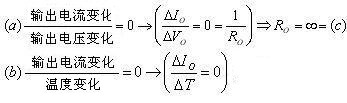
Circuit symbol of constant current source:
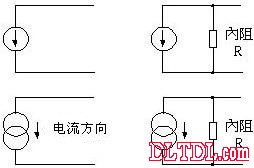
Ideal constant current source
The ideal constant current source has an internal resistance that is infinite, so that its current can flow out completely. The actual constant current source has an internal resistance R.
Constant current characteristics of the triode:
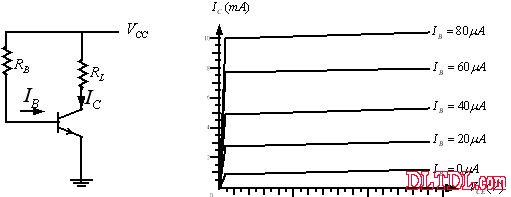
It can be seen from the triode characteristic curve that the IC in the working area is affected by IB, and the influence of VCE on the IC is very small.
Therefore, as long as the IB value is fixed, the IC can be fixed.
The output current IO is the IC that flows through the load.
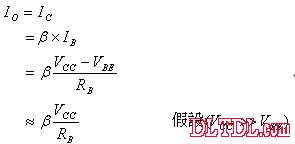
Current mirror circuit Current Mirror:
The current mirror is a circuit in which the input current IS is equal to the output current IO:
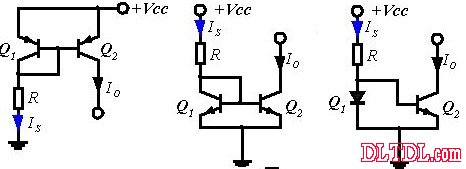
The characteristics of Q1 and Q2 are the same, that is, VBE1 = VBE2, and β1 = β2.
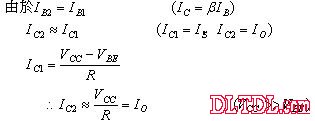
advantage:
The beta of the triode is affected by the temperature, but the current is mirrored by the constant current source, which is not affected by β. The external resistor R is mainly used to determine the output current IO (IC2 = IO) via Q2.
example:
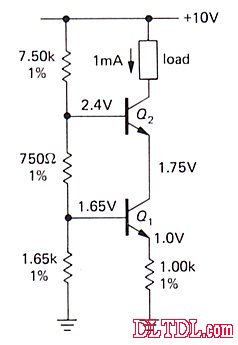
Transistor emitter bias design
Example 1:
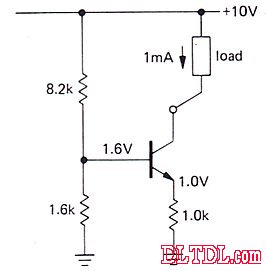
Seen from the left: base bias
So VE=VB - 0.6=1.0V
And because the emitter resistance is 1K, the current flowing through the emitter resistor is
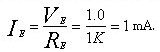
Computer desktop wallpaper
So the current flowing through the load is a stable 1mA
Example 2.
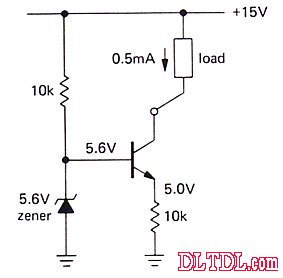
This is a base bias voltage of 5.6V provided by a Zener diode.
VE=VB - 0.6= 5V
Current through mobile phone theme download
Example 3.
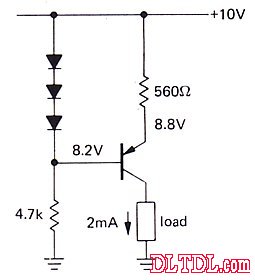
This example is a bit different: the PNP transistor is used to supply current to the load circuit. First, a diode voltage of 0.6 V is used to provide a 8.2 V base bias (10 – 3 x 0.6 = 8.2). The 4.7 K resistor is only used to form the path. And do not want (and will not) have a lot of current flowing through this resistor.
VE=VB + 0.6=8.8V online calculator
The potential difference between the 560 ohm resistor of the PNP crystal is 1.2V, so the current is 2mA.
Crystal constant current source application considerations
If only one transistor can't meet the demand, you can use two triodes to form:
Or
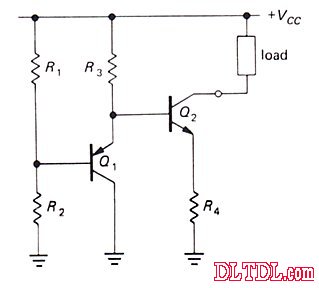
can also be
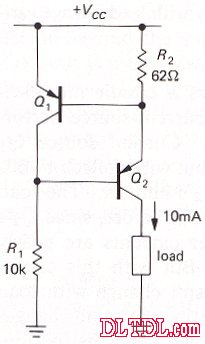
Please note that the constant current source is a two-terminal part. There are also "current regulating diodes" (CRD) available for low current applications. For high current applications, IC regulator series resistors can be used, or The method of using MOSFETs.
Two - way trigger diode, also known as two - end ac device (DIAC), and two - way thyristor at the same time.Because of its simple structure and low price, it is often used to trigger the bidirectional thyristor, and can also constitute overvoltage protection circuits.Construction, symbol and equivalent circuit of a bidirectional trigger diode.
Also commonly used in the overvoltage protection, timing, shift equal circuit, Figure 2 is the overvoltage protection circuit composed of bidirectional trigger diode and bidirectional thyristor.When the transient voltage exceeds the DIAC and Ubo, the DIAC quickly conducts and triggers the bidirectional thyristor to also conduct, so that the following load is protected from overvoltage damage.

DO-35,DIACS,DO-35 Diode,DO-35 package,Small Signal Diode
Changzhou Changyuan Electronic Co., Ltd. , https://www.cydiode.com