At present, low carbonization, intelligence and information technology have gradually become an important research direction for the development of the modern automobile industry. Smart cars are an important technology to promote the sustainable development of the automotive industry, and an inevitable trend in the future development of the automotive industry. However, smart cars do not have current policies and laws to support and regulate. How to standardize the development of smart cars is a major issue that needs to be resolved in the world today.
Therefore, the article analyzes the laws of smart cars and makes recommendations. First, study the current laws and regulations in China, and modify the relevant provisions that hinder the development of autonomous driving. Secondly, on the basis of reference to foreign legislation, combined with China's legal norms and basic national conditions, improve relevant laws to promote the development of smart cars in China.
1. The status quo of smart car developmentThe research in the field of intelligent transportation in the United States, Europe and Japan has been carried out earlier, and in-depth research has been carried out from the aspects of vehicle intelligence and traffic informationization, and a large number of industrialization achievements have been formed.
The United States relies on the government's strong R&D system, focuses on the development of networking, and develops the automotive industry based on V2X-based networking.
Europe has the world's leading manufacturers of automotive electronic components and complete vehicle companies, and its autonomous driving technology is relatively leading. On July 11, 2017, Audi officially released the Audi A8, which is the first production car to reach the level 3 automatic driving level, but it is controversial in use. Whether the technology can serve consumers after mass production needs to be approved by national traffic regulations. Currently, only a few states in Germany and the United States can legally allow autopilot A8 to be on the road.
Japan's transportation facilities are well-founded, and the level of autonomous driving technology is also steadily advancing, moving in parallel with the direction of intelligent traffic road facilities. The Toyota SIP-adus project, the development of self-driving car technology, is a Japanese revitalization plan promoted by the Japanese cabinet government. It will focus on joint industry, academia and government agencies to promote technology development and application. At the same time, it encourages car companies to carry out international R&D cooperation. Nissan has cooperated with many top universities for many years to develop R&D cars.
The US, European and Japanese governments have introduced national strategic plans to promote the development of smart car technology in related fields such as traffic environment and network, and to clarify the development goals, timetables and technical routes of smart cars, for the development and rapid application of smart cars. Established a good environment.
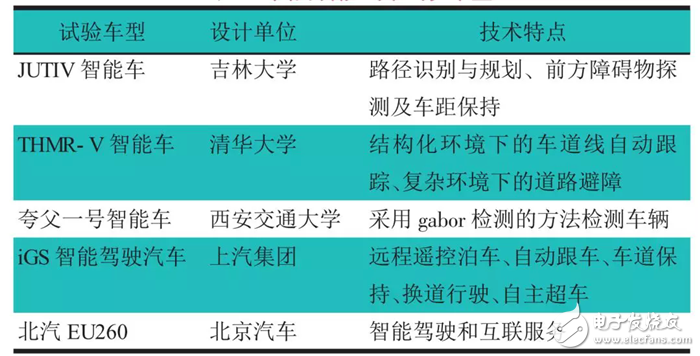
China's autonomous driving technology research and development started late, there are some distances compared with foreign countries, but also achieved a number of phased results. The domestic smart car industry has initially developed, as shown in Table 1. Internet companies have also made great strides in the automotive industry, and companies such as Baidu, ZTE, and SAIC Ali have emerged. Among them, Baidu released an Apollo strategic plan in April 2017 to provide a new software platform for the automotive industry and the autopilot sector. At the same time, some research institutes in China have also actively carried out research, and the National Natural Science Foundation has also strongly supported the research on smart cars.
Table 1 Domestic smart car test models
While smart car technology is rapidly developing and showing great prospects, the pace of smart car legislation is relatively backward. The first Model S car caused the driver to die in the automatic driving mode, and put the smart car legislation into the public. Tesla claims that it has safely traveled more than 200 million kilometers in its Autopilot mode, the first death. The data shows that artificial driving has an average of 150 million kilometers of fatal traffic accidents. Obviously, automatic driving is safer than manual driving. Traffic laws for manual driving are obviously not applicable to smart cars. At present, countries all over the world have carried out related research on autonomous driving policies and regulations.
In March 2016, the United Nations amendment to the auto-driving car in the Vienna Convention (Road Traffic) came into force: in accordance with United Nations vehicle management regulations or in compliance with autonomous driving, autonomous driving technology can be applied to transportation. This rule modification is equivalent to recognizing the legal status of autonomous driving. The revision of the Vienna Convention eliminates regulatory barriers for the application of advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous driving techniques.
The United States is at the forefront of the development of autonomous driving technology, and the pace of legislation is also faster. In 2014, the US Department of Transportation and the US Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) proposed the ITS Strategic Plan 2015 ~ 2019, which provides a direction for the development of the US in the field of intelligent transportation in the next five years. The intelligentization and networking of automobiles is the The core of the strategy is the technical means by which the United States relies on solving traffic problems. Development goals include:
Improve vehicle and road safety;
Strengthen traffic mobility;
Reduce environmental impact;
Promote innovation;
Support traffic information sharing.
In 2016, the US government introduced the Federal Autopilot Vehicle Policy, which is a milestone for the development of autonomous vehicles. The policy encourages states to allow them to independently regulate standards for the application and performance of highly automated driving vehicle (HAV) technology.
According to incomplete statistics, 23 states in the United States have issued 53 bills on autonomous driving:
As early as 2011, Nevada passed the law on the legalization of self-driving cars and issued a series of related regulations, including the determination of the concept of self-driving cars and the process of applying for road test.
At the end of 2016, the latest bill passed by Michigan not only recognized the legitimacy of autonomous driving, but also allowed traditional car companies and technology companies to carry out commercial operations such as vehicle sharing on any section of the state. At the same time, if the self-driving vehicle passes the state's testing and certification, it is allowed to be sold to consumers. The bill aims to promote the research and development of corporate smart cars in the state.
The California State Vehicle Administration announced on 2014-05 that the autonomous vehicles will be allowed to drive on the road from 2015.
On July 27, 2017, the US House of Representatives unanimously passed the two-party Act, the Self Drive Act, to manage the production, testing, and release of autonomous vehicles for the first time. This bill may be the first US federal law to speed up the listing of self-driving vehicles in the United States, with benchmarking value and meaning.
The EU is also actively conducting research to promote the rapid development of autonomous driving by modifying existing laws and regulations on driving:
The UK allows unmanned vehicles to be tested on public roads, requiring vehicles to be equipped with testers and responsible for the safety of the vehicle, as well as for the training of insurance, infrastructure and test personnel.
Spain revised the traffic regulations in 2014, but still requires drivers to be on the road and able to control the vehicle at any time.
A study by the Swedish Ministry of Transport shows that the current law allows for highly automated testing of vehicles, but modifications to the Vehicle Regulations, Driving License Rules and Liability Regulations are still required.
The Finnish Ministry of Transport plans to amend existing road traffic rules to allow autonomous vehicles to be tested in specific areas of public roads, but approval is required.
In May 2017, the German Federal Senate issued a bill to allow autonomous vehicles to test on public roads. In the case of self-driving vehicles that can control the steering wheel and brakes themselves, the driver can leave the steering wheel, surf the Internet, and browse the mail. All are allowed.
3. Key items in smart car legislationIntegrating the key technologies of smart cars and foreign legislative processes, smart car legislation needs to focus on the establishment of four key systems.
3.1 Road test systemIn the testing process of smart cars, the choice of roads and the construction of road facilities should be supported by relevant laws and regulations to ensure the orderly development and smooth progress of the testing process. The system should require that the conditions of the test road meet the test of the basic scene of the smart car, such as straight-line driving in the lane, lane change, overtaking, automatic emergency braking and parking at red light. In the road test process, the vehicle working conditions, the interaction between the vehicle V2V and V2I should be recorded in time, and the improvement work of the smart car should be further carried out based on the above data.
3.2 Insurance systemThe definition of accident liability for autonomous driving has always been a difficult point of legislation, which will lead to delays in compensation. The problem of auto insurance has hindered the development of smart cars. The insurance rules must first address the victim’s compensation. After the accident of the smart car in the automatic driving mode, the victim will get the compensation of the insurance company in the first time, and then solve the responsibility attribution problem. The company can claim the corresponding damages to the specific responsible party for the accident. This will not be because the responsible person is difficult to determine and cannot be legally liable, and will not attack the enthusiasm of developers and consumers because of excessive legal responsibility.
3.3 Operation reporting systemThe vehicle management department supervises the operation of smart cars to ensure the safety of vehicles and people inside and outside the vehicle, and determines the development and innovation of smart cars. Based on this, the vehicle operation reporting system has become one of the key items of legislation. When an accident occurs in a vehicle, regardless of whether the accident causes property damage or casualties, the tester must report the time, place and cause of the accident to the management department. The tester is required to submit an annual summary to the vehicle management department.
The annual summary should have the reason, time and relevant circumstances for the vehicle to switch from autonomous driving mode to manual driving. The report can enable regulators to understand the technical indicators and safety performance of smart cars, obtain practical basis for formulating and improving management content, and enable enterprises to understand specific situations, conduct objective evaluation and research, and improve problems found during testing. Further research and development and upgrade of the technology.
3.4 Information Security SystemThe development of smart car technology requires cross-border integration between the automotive and Internet industries. In the actual operation of smart cars, the automotive industry and the Internet industry need to cooperate intensively to prevent potential security threats. At the same time, relevant laws can be planned in the vehicle's basic security measures to check whether the vehicle uses some of the pre-defined security codes.
4. China's smart car legislation proposalFrom the current policy of China, the state encourages the development of automotive technology and the development of intelligent transportation. However, according to the specific provisions of manual driving, there is no special chapter to stipulate the specifications of smart cars without driving. Since China's auto companies are not allowed to test autonomous vehicles on the road before the introduction of specific policies, it is urgent to develop a programmatic policy that specifically leads the development of smart cars.
China should establish a legal automatic driving system as soon as possible.
1) Need to clarify the concept of automatic drivingDomestic car companies have different definitions of autonomous driving, so the classification is different. The unclear concept will lead to the unclear positioning of the enterprise. Therefore, it is necessary to
Basic Physics Experiment Instrument Series
Basic physics experiment instrument series, used in physics laboratories of colleges and universities.
Basic Physics Experiment Instrument,Light And Optical Instruments,Optical Viewing Instrument,Microscope Light Source Instrument
Yuheng Optics Co., Ltd.(Changchun) , https://www.yhenoptics.com