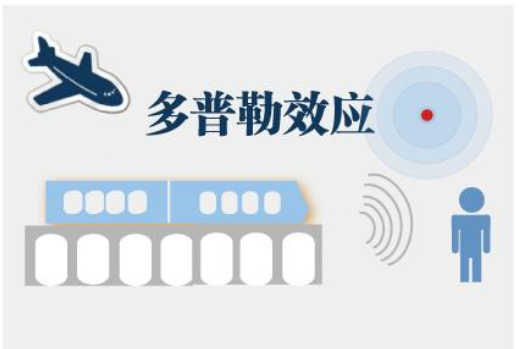
Doppler effect
Analogy: When Zhong Duan (the pseudonym of the terminal) first joined the work, he was very afraid that the leader Ji Zhan (the pseudonym of the base station) would ask about work-related questions. When Zhong Duan approached Ji Zhan at a certain speed, he felt his heartbeat frequency increased (frequency deviation was positive); when he left Ji Zhan, his heartbeat gradually eased (no frequency deviation). This process is similar to the Doppler shift effect.
The Doppler effect means that the receiving frequency of radio waves becomes higher when the wave source moves quickly to the observer, similar to the increase in his heartbeat frequency when the leader is close to the clock end; while the receiving frequency becomes lower when the wave source is far away from the observer, like a clock When he was far away from the leader, his heart rate gradually became the same.
When the sirens of the police car and the engine of the racing car approach us at a certain speed, the sound will be harsher than usual; when we are far away, the sound will be softened; the same thing, you can hear the harshness when the train passes by The change in sound illustrates the existence of the Doppler effect.
Multipath effect
Analogy: Everyone used to play with soil when they were young. Pour water on the top of a small mound. The water flows from everywhere. A lot of the water seeps into the soil or flows to different directions and is lost. Some of the water flows through different paths and at different times. Sink to a low-lying place.
The multipath effect of radio waves means that there are often many transmission paths with different delays and different losses from the transmitting end to the receiving end, which can be direct, reflected or diffracted. The same signal of different paths will be superimposed on the receiving end. The phenomenon of increasing or decreasing the energy of the received signal.
White Noise
Analogy: When the old electrical equipment such as the radio is turned on, you may hear a "buzzing" sound;
White noise refers to noise whose power spectral density is uniformly distributed in the entire frequency domain. Random noise with the same energy at all frequencies is called white noise. From the frequency response of our ears, it sounds like a very bright "sizzle" sound. White noise is a random signal or random process with a constant power spectral density. The power of this signal in each frequency band is the same. The ideal white noise has an infinite bandwidth, so its energy is infinite. This is impossible in the real world, but it makes mathematical analysis more convenient. Generally, as long as the spectral width of a noise process is much larger than the bandwidth of the system it acts on, and its spectral density in this bandwidth can basically be considered as a constant, it can be treated as white noise. Thermal noise can be considered white noise.
Gaussian white noise (and Rayleigh distribution)
Analogy: Thermal noise and shot noise are Gaussian white noise.
Gaussian white noise: If a noise, its amplitude distribution obeys the Gaussian distribution, and its power spectral density is uniformly distributed, it is called Gaussian white noise. The envelope of the sum of two orthogonal Gaussian noise signals obeys the Rayleigh distribution. The amplitude obeys the Gaussian distribution, that is, the amplitude probability density distribution is axisymmetric with the mean value, the largest at the mean value, and the curve inflection point at a variance. The linear combination of Gaussian noise is still Gaussian noise. When summing the noise generated by independent noise sources, it can be added directly by power.
Phase noise
Analogy: After the flights from Beijing to Shanghai are arranged, they take off and land at a fixed time every day, repeating itself again and again. However, due to weather conditions, flights could not take off and land normally, and many flights were delayed relative to normal times.
Phase noise refers to the random change in the phase of the system output signal caused by various noises in the system (such as various radio frequency devices). The three elements describing radio waves are amplitude, frequency, and phase. Frequency and phase influence each other. Ideally, the fluctuating period of a fixed-frequency wireless signal is fixed, just like a normal flight of an airplane, the take-off time is fixed. In the frequency domain, a pulse signal (the spectral width is close to 0) is a sine wave of a certain frequency in the time domain.
But the actual situation is that the signal always has a certain spectral width, and due to the influence of noise, there is also the power of the signal far away from the center frequency, just like a flight delayed for more than 1 hour. Signals far away from the center frequency are called sideband signals, and sideband signals may squeeze into adjacent frequencies, just as a delayed flight may squeeze into the time of other flights and affect it. So this sideband signal is called phase noise.
How does phase noise describe its magnitude? The ratio of the power in the unit bandwidth to the total signal power within a certain range of the offset center frequency, in dBc/Hz. Just as you want to assess the impact of weather on flights on a certain day, you can define the ratio of flights delayed more than 1 hour to the total number of flights. The smaller the ratio, the better. Thermal noise in the RF device system may cause phase noise. The magnitude of phase noise can measure the pros and cons of radio frequency devices. The smaller the phase noise, the better the RF device.
Signal to noise ratio
Analogy: Wukong asked Bajie: "What kind of girlfriend are you looking for?" Bajie replied: "Of course the more beautiful the better."
Wukong asked: "Let you chase for a lifetime, do you want it?" Ba Jie whispered, "I dare not ask for it."
Wukong asked the Drifter: "What kind of Internet speed do you want?" The Drifter replied, "Of course the faster the better."
Wukong asked: "One bit requires you two dollars, can't you make it?" The Drifter whispered, "Don't dare to make it."
Wukong asked Tang Seng, "What kind of mount do you want?" Tang Seng replied, "The faster the better, the more fuel-efficient, the better, and the safer the better."
Wukong asked: "I want you to sell the house in Beijing and buy a car with a face and a brand. Can you still buy it?" Tang Seng whispered, "Don't dare to buy it."
Wukong concluded: "When you want to get benefits, you will definitely pay a price. What you have to consider is whether the benefits you get compared with the price you pay are appropriate, that is, the issue of cost performance. It is not that the more benefits, the better, but The higher the price/performance ratio, the better."
The signal-to-noise ratio is simply the ratio of useful signal to interference noise. During the transmission of useful signals, various noises will inevitably be introduced, at least thermal noise. When a radio frequency device such as an amplifier amplifies the useful signal power, it will inevitably amplify the corresponding noise. Signal/Noise (Signal/Noise), usually expressed in SNR, the signal-to-noise ratio expressed in power under the same radio frequency is the square of the signal-to-noise ratio expressed in voltage, and generally refers to the ratio of power in engineering. If expressed in decibels (dB), the signal-to-noise ratio expressed in power is 2 times the signal-to-noise ratio expressed in voltage. The larger the signal-to-noise ratio, the better.
Application: It is not recommended to buy speakers and MP3 with a signal-to-noise ratio (voltage) below 80dB.
Noise Figure
Analogy: After a few years after Ba Jie and Miss Gao were married, Wukong asked Ba Jie: "How about it, how is the little life?" Ba Jie looked miserable and said, "Don't mention it, Miss Gao has reduced the price/performance ratio a lot. I’ve lost my temper a lot, my life has been lazy, and I continue to ask for higher living expenses.†Miss Gao’s price/performance ratio before marriage is many times higher than after marriage. This multiple can be called the Marriage Box Coefficient. Can describe the quality of marriage.
The radio frequency device itself will add noise, and the signal-to-noise ratio at the input end will be higher than that at the output end. The ratio of the input signal-to-noise ratio to the output signal-to-noise ratio is the noise figure of the radio frequency device.
The noise figure can measure the radio frequency (RF) performance of receivers and amplifiers, and represents the loss of signal useful power and the amplification of noise power after radio frequency devices. The noise figure of the base station is about 3~5dB, and the noise figure of the user mobile station is about 7~9dB.
Additive noise
Analogy: The Wanli Yellow River is formed by the gradual convergence of trickles formed by high mountain snowwater. There are three more important sources: one is Zhaqu, the other is the Yuguzonglie Canal, and the third is Kariqu. When Zhaqu dries up, Kariqu still has plenty of water.
Additive noise acts on useful signals through direct power superposition, but its existence is independent of useful signals. Regardless of whether there are useful signals or not, additive noise always exists in radio frequency devices and affects the quality of normal communication.
In general communication, random additive noise is regarded as the background noise of the system; from the source, additive noise can be divided into radio noise, industrial electrical noise, natural noise, and internal thermal noise of radio frequency devices. The radio interference frequency is fixed and can be avoided as much as possible by strengthening the management of radio frequency. Industrial electrical noise comes from various electrical equipment, but the interference spectrum is concentrated in a lower frequency range. Choosing a higher power frequency can prevent interference. Natural noise comes from lightning, sunspots and cosmic rays. This type of noise is difficult to avoid. The internal thermal noise is caused by the irregular thermal motion of electronic devices. It can be described mathematically by a random process, which can also be called random noise.
Shannon's Theorem
Analogy: What does the speed of a car on a city road have to do with? It is related to the width of the road, to the power of your own car, and to other interference factors (such as the number of vehicles and the number of red lights).
Shannon's theorem is the most basic principle of all communication systems: C=Blog2(1+S/N)
Among them, C is the available link speed, B is the bandwidth of the link, S is the average signal power, N is the average noise power, and S/N is the signal-to-noise ratio.
Shannon's theorem gives the relationship between the upper limit of link speed (bits per second (bps)) and the link signal-to-noise ratio and bandwidth. Shannon's theorem can explain the difference in the maximum throughput of a single carrier supported by various 3G systems due to different bandwidths.
Skin effect
Analogy: After the heavy rain, water accumulated in the middle of the dirt road in the countryside, and everyone had to line up along the roadside to pass. The effective passage area of ​​the road is reduced due to stagnant water, which affects people's travel efficiency.
Since the inductive reactance inside the conductor hinders the alternating current more than the surface, when the alternating current passes through the conductor, the current density of each part is not uniform, and the current density on the surface of the conductor is large (reduce the cross-sectional area and increase the loss). This phenomenon is called For the skin effect. The higher the frequency of alternating current. The skin effect is more pronounced. The frequency is high to a certain extent. It can be considered that the current flows completely from the surface of the conductor.
Practical application: Hollow wires replace solid wires, saving materials; in high-frequency circuits, multiple strands of mutually insulated thin wires are woven into bundles to weaken the skin effect.
Coherence time
Analogy: Twin brothers who wear the same clothes and look similar appear side by side at the same time, which is difficult for ordinary people to distinguish. If they take a photo with the same action side by side, it seems that there is a double image in the picture alone, and the person watching it thinks that they are dazzled.
The coherence time is the range of the maximum time difference within which the channel remains constant. The same signal from the transmitting end reaches the receiving end within the coherence time. The fading characteristics of the signal are completely similar, and the receiving end considers it to be a signal. If the autocorrelation of the signal is not good, interference may also be introduced, which is dazzling if the ghost is similar to a photograph.
To understand from the perspective of transmit diversity: time diversity requires that the time of two transmissions is greater than the coherence time of the channel, that is, if the transmission time is less than the coherence time of the channel, the two transmitted signals will experience the same fading, and diversity has the effect of anti-fading Does not exist anymore. Each chip of TD-SCDMA has a time length of 0.78us, that is, the coherence time between chips is 0.78us. If the same signal reaches the receiving end through different paths, the chip will have multipath diversity effect if this time is exceeded; otherwise, Form self-interference.
Coherence bandwidth (1/coherence time)
Analogy: Half of a section of the city’s busy traffic arteries is being renovated. As the road becomes wider and narrower, the speed of passing vehicles needs to be slowed down. Some vehicles are squeezed onto the bicycle lane, and some simply detour.
The coherence bandwidth is an important parameter that characterizes the characteristics of a multipath channel. It refers to a specific frequency range in which any two frequency components have a strong amplitude correlation, that is, within the coherent bandwidth range, Multipath channels have constant gain and linear phase.
In a wireless communication system, if the bandwidth of the signal is smaller than the coherent bandwidth of the channel, the received signal will experience a flat fading process. At this time, the spectral characteristics of the transmitted signal can still remain unchanged in the receiver. If the bandwidth of the signal is greater than the coherent bandwidth of the channel, the received signal will experience frequency selective fading. At this time, some frequencies of the received signal gain greater gain than other components, causing distortion of the received signal and causing inter-symbol interference .
Power Control
Analogy: When you want to stop the friend Zhang Hua who is walking in front of you, you call out his name: "Hey, Zhang Hua!" When you find that he is not listening, you will raise your voice and call his name. If Zhang Hua has heard your voice, he tells you: "Speak down to scare others.", you will lower your voice and talk to him.
Power control can ensure that the transmitted power of each user reaches the base station to keep it to a minimum, which not only meets the minimum communication requirements, but also avoids unnecessary interference to other users' signals and maximizes the system capacity. When the mobile phone moves in the cell, its transmission power needs to be changed; when it is closer to the base station, it needs to reduce the transmission power to reduce interference to other users, when it is far away from the base station, it should increase the power to overcome Increased path loss.
Diffraction
Analogy: See "Direct Wave"
When the wireless path between the receiver and the transmitter is blocked by sharp edges, the phenomenon that radio waves travel around the obstacle is called diffraction. During diffraction, the path of the wave changes or bends. The secondary waves generated by the blocking surface are scattered in the space, even on the back of the blocking body. Diffraction loss is the loss caused by various obstacles to the transmission of radio waves.
Direct wave
Analogy: In the sport of billiards, many laws are very similar to the laws of electromagnetic waves. If it hits the center of the ball directly, if there is no obstruction, the ball will move in a straight line; if the ball hits the edge of the table, it will run according to the law of reflection angle equal to the angle of incidence; if the cue ball is opposite to another ball Cut, according to the strength and direction, it can bypass the ball in the line of sight, much like diffraction; assuming that the distance between many balls in a range is not more than one ball, when the cue ball hits the middle of these balls, it will arouse a lot The ball moves in different directions, much like scattering.
Feeling: The most fundamental laws of many things in nature are interlinked. This is the reason why Tao is Tao. However, the law we have revealed is always lacking, and it is "very Taoist." The most fundamental way can only be realized.
The radio waves that reach the receiving point along a straight line from the transmitting antenna are called direct waves. The propagation of radio waves in free space is the propagation of radio waves in vacuum, which is an ideal propagation condition. When a radio wave propagates in free space, it can be considered as a direct wave propagation, and its energy will neither be absorbed by obstacles nor reflected or scattered.
Reflection wave
Analogy: See "Direct Wave"
Application: When selecting stations for high-speed railway wireless coverage, attention should be paid to the incident angle of radio waves. The alternative site should not be too far away, otherwise the incident angle is too large, and the refractive power into the carriage will be reduced. Generally, a station site about 100 meters away from the railway is selected (other factors need to be considered).
The wireless signal is reflected by the ground or other obstacles to reach the receiving point, which is called reflected wave. Reflection occurs on the surface of the earth, buildings and walls. Reflected waves only occur at the interface between two propagation media with different densities. The greater the difference in interface media density, the greater the reflection and the smaller the refraction. The smaller the incident angle of the wave, the smaller the reflection and the greater the refraction. The combination of direct waves and reflected waves is called space waves.
Scattered Wave
Analogy: I saw a car accident not long ago. Many vehicles were driving and the distance between each other was not enough to pass another vehicle. But there was a car behind it rushing into the middle of many vehicles without any slowing down, and the current situation was terrible.
Scattering occurs when there are objects smaller than the wavelength in the medium through which radio waves travel, and the number of blocking objects per unit volume is very large; scattered waves are generated on rough surfaces, small objects or other irregular objects. In an actual communication system, leaves, street signs, and lamp posts can cause scattering.
Fresnel Zone
Analogy: Sometimes, I feel that the most effective vision range of the human eye is also an ellipsoid. Although things other than the ellipsoid can be seen, it is not particularly clear anymore. For a well-trained shooter, his effective vision range must be concentrated in the ellipsoid with a very small radius between him and the target.
Application: When surveying the wireless site, be sure to pay attention to whether the coverage area has obstacles larger than the Fresnel radius. Especially large billboards, tall buildings and other obstacles.
The Fresnel zone is an ellipsoid, and the transmitting and receiving antennas are located on the two focal points of the ellipsoid. The radius of this ellipsoid is the first Fresnel radius. In free space, the electromagnetic energy radiated from the transmitting point to the receiving point mainly propagates through the first Fresnel zone. As long as the first Fresnel zone is not blocked, the propagation conditions similar to free space can be obtained.
In order to ensure the normal communication of the system, the height of the transceiver antennas must be such that the obstacles between them do not exceed 20% of their Fresnel zone as much as possible, otherwise the multipath propagation of electromagnetic waves will have an adverse effect, resulting in a decrease in communication quality, or even Interrupt communication.
UHF UHF
UHF: Decimeter band, refers to UHF radio waves with a frequency of 300~3000MHz.
Radio waves are distributed between 3 Hz and 3000 GHz, and are divided into 12 bands in this spectrum. The frequency propagation characteristics in different frequency bands are not the same. The smaller the frequency, the smaller the propagation loss, the longer the coverage distance, and the stronger the diffraction ability. However, low frequency band frequency resources are tight and system capacity is limited. The high frequency band has abundant frequency resources and large system capacity; however, the higher the frequency, the greater the propagation loss, the smaller the coverage distance, the weaker the diffraction ability, the greater the technical difficulty of implementation, and the higher the cost of the system.
Compared with other frequency bands, the UHF frequency band has a better compromise between coverage effect and capacity, and is widely used in the field of mobile communications.
Shadow effect
Analogy: When the warm sun shines on the earth, trees and houses have shadows. This shadow is not completely dark, but a kind of light with much weaker intensity.
On the propagation path, when radio waves encounter obstacles such as uneven terrain, buildings of varying heights, tall trees, etc., behind the obstacles, shadow areas with weaker radio signal field strength will be formed. This phenomenon is called the shadow effect.
Slow fading
Analogy: In the process of stock market decline, although the time-sharing curve fluctuates sharply, the 5-week line changes relatively slowly.
During the propagation of radio waves, the median value of the signal strength curve changes slowly, which is called slow fading. Slow fading reflects the median value after the weighted average of the instantaneous values, and reflects the average change of the receiving level on the order of hundreds of wavelengths in the medium range, and generally follows a lognormal distribution.
Reasons for slow fading:
1) The main reason for slow fading is path loss;
2) Signal fading caused by shadow effect:
Fast fading
Analogy: In the process of stock market decline, the instantaneous value of stock prices changes drastically, much like a fast decline.
Fast fading is the instantaneous rapid fluctuation and rapid change of the received signal field strength value. Fast fading is caused by the superposition of multipath propagation signals caused by various terrains, ground objects, and moving objects at the receiving point. Because the phase, frequency and amplitude of the received multipath signals are different, the amplitude of the signal after superposition fluctuates sharply. . When the mobile station is operating at high speed, the carrier frequency range of the received wireless signal changes with time, which can also cause drastic changes in the amplitude of the superimposed signal. In other words, multipath effects and Doppler effects can cause fast fading.
Generally fast fading can be subdivided into:
1) Multipath effects cause spatial selective fading, that is, different locations and different transmission paths have different fading characteristics;
2) The change of carrier frequency causes the carrier width to exceed the coherent bandwidth, and the signal distortion caused is called frequency selective fading;
3) The Doppler effect or multipath effect can cause the time difference of different signals to reach the receiving point to be different. If the coherence time is exceeded, the signal distortion caused is called time selective fading.
Time dispersion
Analogy: A girl had a handsome boy who liked her first, and after a while, another handsome boy liked her. She didn't know how to choose.
In wireless communication, co-frequency interference caused by the difference in space transmission time between the main signal and other multipath signals arriving at the receiver. Time dispersion can make the wireless signal reflected from an object far from the receiving antenna reach the receiving end several symbols later than the direct signal, which may cause inter-symbol interference. For example, "1" affects "0" and causes the receiver to decode errors.
Propagation loss
Analogy: Anyone in the long-distance vegetable trafficking business knows that if the cabbage purchased from the farmers is 1 cent per catty, plus the intermediate links of transportation, stall fees, taxes, and packaging fees, it will reach the end consumers. The catty is at least 50 cents. In the end, the vegetable seller needs to subtract all the loss of profits from the total turnover.
For a given frequency wireless system, the wireless propagation loss is mainly the path loss (Path Loss) that changes with distance. The three most basic propagation mechanisms that affect the path loss are reflection, diffraction, and scattering, that is, reflection loss (Reflection Loss). ), Scattered Loss, Clutter Loss. If electromagnetic waves pass through obstacles such as walls, cars, trees, etc., penetration loss (Penetration Loss) needs to be considered. If the mobile phone is used close to the human body, the body loss (Body Loss) should also be considered.
The environmental factor coefficient n of path loss generally varies with the propagation environment. Generally, it is 4 to 5 in dense urban areas, 3 to 4 in ordinary urban areas, and 2.5 to 3 in suburbs. In the actual wireless environment, the height of the antenna can affect the path loss. Generally, the height of the transmitting antenna or receiving antenna is doubled, which can compensate for the propagation loss of 6dB.
The reflection loss varies with the reflection surface. The reflection loss of the water surface is 0~1dB, the reflection loss of the wheat field is 2~4dB, and the reflection loss of cities and mountains can reach 14dB~20dB.
The diffracted wave spreads around the diffraction point and spreads to all directions except obstacles, and the loss varies greatly in different situations. The ground object loss is mainly caused by surface scattering, and the loss depends on the specific situation.
The penetration loss has a large relationship with the material of the building and the angle of incidence of electromagnetic waves. Generally, the barrier of the partition wall is 5-20dB, the barrier of each floor is 20dB, the thick glass is 6-10dB, and the penetration loss of the train carriage is 15-30dB , The penetration loss of the elevator is about 30dB. Human body loss generally takes 3 dB, that is, when radio waves pass through the human body, half of the energy is absorbed by the human body.
SPM model
Analogy: In the pre-Qin era, the writings of the various princes were not unified, and it was very inconvenient for people from different countries to communicate. Finally, Qin Shihuang told the people of the world that the characters he used were standard characters, and everyone used this type of character uniformly.
There are many forms of wireless propagation models, and there are many scopes of application. Due to the inconsistency in form, it is very inconvenient for wireless engineers to use, and it is difficult to have a unified understanding of the same wireless environment.
The introduction of the SPM model solved this problem. The SPM model is suitable for a relatively wide frequency range from 150MHz to 2GHz, as well as various wireless environments from dense urban areas, ordinary urban areas, suburbs, and rural areas. Therefore, it is currently widely used.
Peak-to-average ratio
Analogy: In a village, there are richer and poorer families, but most of them are ordinary people with middle income. The ratio of the wealth of our richest family to the average wealth of the village or the sum of the wealth of the poorest family The ratio of average household wealth can measure the degree of polarization between the rich and the poor in the village.
However, from a national perspective, it is not appropriate to compare the wealth ranked first in the Hurun rankings with the average income of Chinese households, and it cannot fully measure the gap between the rich and the poor in China. If we use the average wealth of 1% of China's wealthy class and the average income of Chinese households, some problems can be explained. If the average annual income of a Chinese family is 30,000 yuan, and the annual income of the richest richest family is 3 billion, the ratio of 3 billion to 300 million is 100,000 times. If expressed in dB, it is 50 dB.
If we study the distribution of the wealth of the rich in various natural villages across the country to illustrate the level of economic development in different provinces, we can also use the concept of peak-to-average ratio, that is, the wealth of the richest village is compared with the average of the wealth of all the villages. That is to say, the peak-to-average ratio must indicate what kind of peak-to-average ratio, whether the unit is absolute ratio or dB value.
Explanation: The wireless signal observed in the time domain is a sine wave with constantly changing amplitude. The amplitude is not constant. The peak amplitude of the signal in one period is different from the peak amplitude in other periods. Therefore, the average power and peak value of each period The power is not the same. In a relatively long period of time, the peak power is the maximum transient power with a certain probability, and the probability is usually 0.01%. The ratio of the peak power under this probability to the total average power of the system is the peak-to-average ratio. The PAR at a probability of 0.01% is generally called the crest factor (CF CREST Factor, CF).
To understand the concept of peak-to-average ratio, you need to pay attention to the following points:
1. Since the peak-to-average ratio of power is the square of the peak-to-average ratio of voltage, PAR generally refers to the peak-to-average ratio of power, but it is also used as the peak-to-average ratio of voltage in books.
2. If the power amplitude does not change with time, that is, the "maximum envelope" and "average envelope" are equal everywhere, that is, the peak-to-average ratio of the "constant envelope" signal is 1 or 0dB.
3. If only one period of pure sine wave of the wireless signal is considered, the power peak-to-average ratio is 2, which is 3dB; and the crest factor CF of its voltage is the square root of the power peak-to-average ratio 1.414. But in general, the peak-to-average ratio rarely refers to this situation.
3. Modulation technology and multi-carrier technology may bring about a larger peak-to-average ratio. Too large peak-to-average ratio is not a good thing, and it will affect the application efficiency of many radio frequency devices.
Radio Frequency RF
Analogy: If you want to travel in the air, you can use an airplane as a carrier. The condition for an airplane to take off is that it must have a certain speed, and the speed can only be increased by passing a certain length of airport runway.
For information to be transmitted in the air, radio waves must be used as carriers, but when the frequency of radio waves is lower than 100 KHz, the waves will be absorbed by ground objects, and the receiving device is also very complicated. Only radio waves that reach a certain frequency can be transmitted over long distances in the air, and information can be easily received. Radio frequency is a high-frequency alternating electric wave that can be emitted, and the frequency ranges from 300KHz to 30GHz.
Transmission cables that can transmit radio frequency signals are radio frequency lines, such as feeders used in engineering. The transmission of modulated high-frequency radio waves in the radio frequency line is called radio frequency wired transmission. The radio frequency line is connected with the antenna, and the radio frequency signal is transmitted or received into the air through the antenna.
distortion
Analogy: Everyone is more familiar with the story of the emperor's new clothes. Adults all praise the emperor's clothes for being beautiful, but only the children say: In fact, he didn't wear anything. When the child was first able to speak, he saw the neighbor’s apple and wanted to eat it. He cried and wanted to eat the apple, expressing his intentions truthfully. When I was six or seven years old, I still wanted to eat the neighbor’s apples, but said, “Your apples are very beautiful.†When I grow up, although I want to eat the neighbor’s apples, to show that I don’t lack apples. Dodge said: "I don't eat, I really don't eat." Children truly tell what they see or tell their true thoughts, this is called innocence; while adults conceal their true seeing and true thoughts, this It is called loss of innocence (frankness), or distortion.
The so-called distortion is the loss of reality, or the distorted manifestation of the real thing. When the signal passes through the RF transceiver channel, due to the introduction of additive noise and multiplicative noise, there will be a certain degree of distortion of the transmitted signal, which is the distortion of the wireless signal. The distortion of wireless signals can be divided into linear distortion and nonlinear distortion.
ZGAR PCC
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
From production to packaging, the whole system of tracking, efficient and orderly process, achieving daily efficient output. We pay attention to the details of each process control. The first class dust-free production workshop has passed the GMP food and drug production standard certification, ensuring quality and safety. We choose the products with a traceability system, which can not only effectively track and trace all kinds of data, but also ensure good product quality.
We offer best price, high quality Vape Device, E-Cigarette Vape Pen, Disposable Device Vape,Vape Pen Atomizer, Electronic cigarette to all over the world.
Much Better Vaping Experience!

E-Cigarette Vape Pen,Disposable Device Vape,Vape Pen Atomizer,Latest Disposable E-Cigarette OEM vape pen,OEM electronic cigarette
ZGAR INTERNATIONAL(HK)CO., LIMITED , https://www.sze-cigarette.com