Around 8.4 billion IoT smart devices worldwide at the end of 2017, an increase of 31% over 2016. In 2020, the total number of IoT smart devices will increase to 20.4 billion. The market for smart devices and application services for the Internet of Things will expand to $200 billion in 2017.
In China, many investment consulting agencies are constantly paying attention to the Internet of Things market. Many technology companies have promoted their IoT products in security, automotive, construction, and finance. After paying attention to and testing some software and hardware products and services of the Internet of Things, it was concluded that most of the products on the market lack some basic security genes. For customers with high security needs, such as high-end retailers, factories, banks, security and the public security industry, IoT products cannot be used in these industries.
A qualified security IoT product requires the following basic security capabilities:
Anti-intrusion and extortionA qualified IoT device or service requires a rigorous anti-hacking and extortion module. In 2015, 220,000 Apple mobile phone users worldwide were hacked, most of them Chinese. Compared with the relatively complete account system of Apple's mobile phone, most of the cameras, routers, sensors, etc. on the market have simple user name and password settings. These terminal IoT devices will be easily attacked after being connected to the external network.
Anti-data fraud and tamperingIn 2010, the Stuxnet worm tampered with data from the logic controller, causing delays in Iran’s nuclear program. In 2013, Syrian hackers broadcast Obama’s fake fake news on the official Twitter account, causing the Dow Jones index to fluctuate violently. These examples are all serious effects of data transformation. For some high-risk industries, such as chemical plants, security and public security, the ability of any IoT device to prevent data falsification and tampering will be tested.
Anti-botnetMost IoT devices on the market are connected to the Internet, and the control rights of the devices are assigned by users. Due to the ease of use of individual users in security settings, device control rights can easily fall into the hands of hackers, resulting in the proliferation of zombie computers. In 2011, the US Federal Bureau of Investigation cracked the Coreflood malicious program, which caused some 2 million personal computers worldwide to become part of a botnet.
In response to some of the basic security requirements for IoT devices described above, IoT devices and service providers need to be strengthened in the following areas:
Internet of Things Equipment Monitoring SystemFor each intelligent hardware connected to the IoT, the product provider should provide the ability to connect to an independent device monitoring system. This equipment monitoring system should have the following basic functions:
l Device hardware status monitoring
l Device network connection status monitoring
l In-device software function status monitoring
The IoT device itself also needs to enhance the device's own account authentication system, including the following features:
l Force users to modify the default account and password
l Increase the intrusion detection module
l Electronic signature authentication
Relying on the underlying hardware information of the IoT device, the device authentication system of the Internet of Things can be implemented by referring to the physical anti-copy technology (PUF) hybrid device cryptosystem. This kind of IoT hardware with strong security features is the foundation of the IoT security solution.
The principle of PUF itself relies on the physical characteristics of SRAM. After the electrical components are energized, the base organization is also activated, and switches between 0 and 1 bits. This bit signal is different in each wafer due to the slight difference in physics. The content of the bit signals generated by these starts can be converted into unique "biometrics" of the device and used as the basis for authentication of the underlying device.
The system authentication method combined with PUF is as shown in Figure 1.

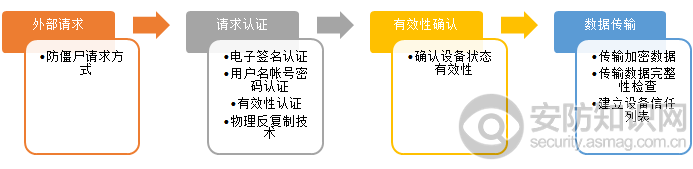
Legend 1
At the same time, in the data storage protection of the device, we are building the data storage encryption protocol of the embedded blockchain technology based on the above IoT hardware, and the principle of the system is created:
Imagine a 100 distributed database cluster IoT device deployed in the customer's intranet. If these devices are controlled by hackers, the data owners in the 100 devices become hackers, and all nodes are in the customer. In the net, so this hacker can let 100 devices do anything, and hackers have absolute access to these devices. This situation is not allowed to happen.
The device is now set up to break the control rights of the 100 devices, and the node data of each control authority is the same, that is, completely redundant, and all nodes are in the wide area network, in other words, this 100 The nodes are untrusted and there is no entity, it has absolute usage rights.
In addition, the following rules should be revised, as shown in Figure 2.
l The data exchange process of each device node is not tampered with;
l Each device exchange history cannot be tampered with;
l The data of each device node is synchronized to the latest data and acknowledges the latest data that has been consensus; l Based on the principle of minority majority, the data maintained by the whole node objectively reflects the exchange history.
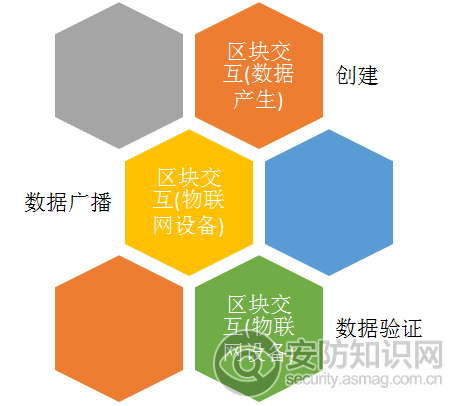
Legend 2
The Internet of Things itself is still a new thing, and it needs to be formulated and improved at the national level. At this stage, the landing and improvement of IoT products depends on the users themselves. Only IoT products that combine management processes and appropriate hardware and software technologies can increase the efficiency, security, flexibility, and automation of IT equipment.
Elcb Breaker,Elcb Circuit Breaker,Earth Leakage Breaker,Earth Leakage Protection
ZHEJIANG QIANNA ELECTRIC CO.,LTD , https://www.traner-elec.com